Introduction
Schedule 40 steel pipe is the most prevalent pipe schedule. It’s widely used in water and gas lines, and it can be galvanized but isn’t essential. It might also appear when there is a need for adornment or support.
It creates a good pipe due to its versatility and performance strength. Let’s take a look at what schedule 40 steel pipe is and why it might be the best option for many projects now that it’s under so much stress.
What Is a Pipe Schedule and How Does It Work?
A pipe schedule (SCH) is a measurement of a steel pipe’s nominal wall thickness.
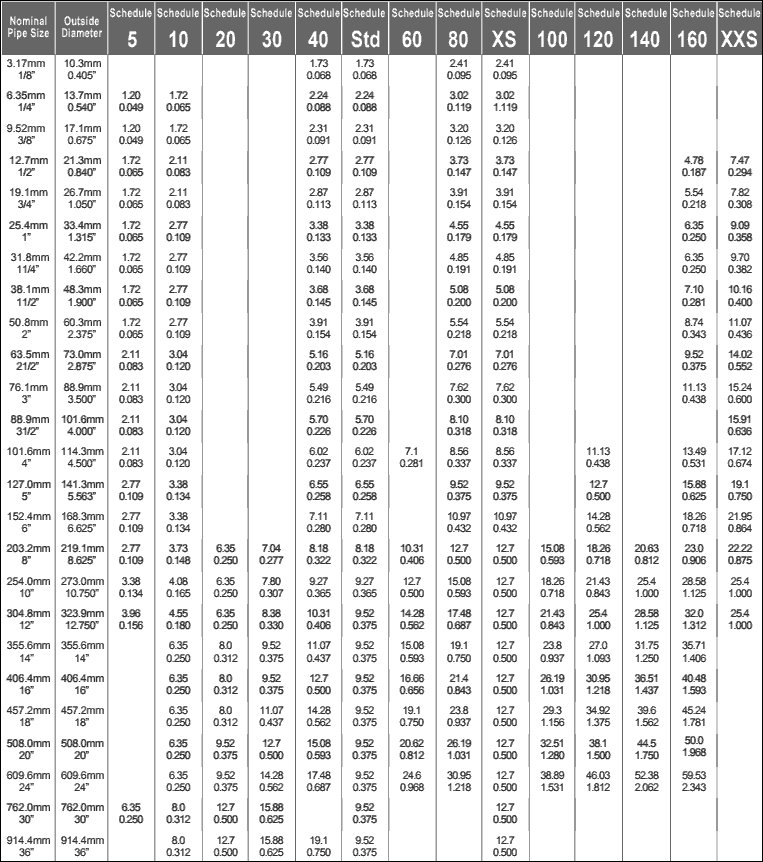
Previously, metal fabricators used three pipe sizes: standard, extra strong, and double extra strong. Having these three unknown dimensions, however, was insufficient. Steel pipes now come in 14 different schedules.
The most commonly used schedule is 40.
What exactly does the term “schedule 40 pipes” mean?
The numerals on the pipes have an unknown dimensionality. To put it another way, the designation SCH 40 does not imply a pipe diameter of 40 millimeters or 40 inches.
The parameters of each schedule are determined by the ASME B36.10M standard, which defines seamless and welded steel pipe specifications. ASME B36.10M specifies the numerical designations for each size.
Schedule 40 Steel Pipe Grades
Most schedule 40 steel pipe is made out of mild steel. This means it has between 0.2 and 0.25 percent carbon in it. This is very low, so the resulting alloy is mostly iron.
Galvanizing SCH 40 steel pipe makes it more resistant to corrosion. Galvanizing means putting a layer of zinc on the steel. If this isn’t an option, you can also get schedule 40 pipe made of stainless steel.
Most people think of SCH 40 steel pipe when they hear the term “A53 steel pipe,” but there are other grades.
Dimensions of Schedule 40 Steel Pipe
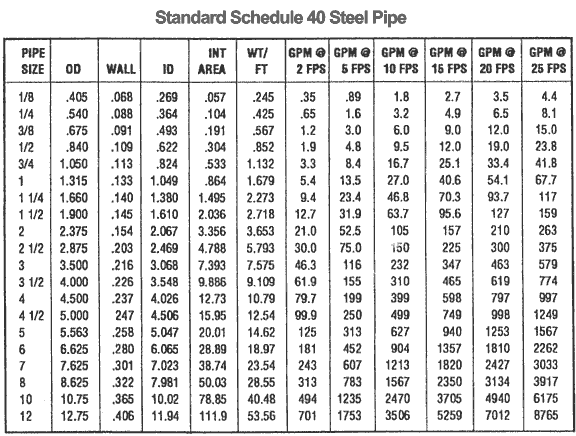
The thickness of a wall is determined by its thickness and its outer diameter. A 1/8th-inch nominal size schedule 40 pipe has an outside diameter of 0.405 inches and a wall thickness of 0.068 inches. Per square foot, it weighs 0.245 pounds.
The 4-inch schedule 40 steel pipe is the most common. The outer diameter of this pipe is 4.5 inches, the wall thickness is 0.237 inches, and the weight per foot is 10.79 pounds.
What is the diameter of schedule 40 steel pipe?
This steel pipe comes in a variety of sizes. The length, nominal diameter, real interior diameter, and real external diameter of the pipe are all within permissible parameters.
A 2.5-inch schedule 40 pipe, for example, will have a real internal diameter of 2.469 and a real outside diameter of 2.875.
At almost any length, we can supply or cut scheduled 40 steel pipes.
Schedule 40 Steel Pipe’s Weight
The average weight per foot is 1.68 pounds.
What is the greatest weight a schedule 40 steel pipe can withstand?
A lot of things influence how much weight it can support. The yield strength of a standard pipe made of A53-grade black steel is 30,000 pounds per square inch.
Given this information…
Consider a four-foot span with a one-inch pipe. The centre should be able to hold 300 pounds with a one-quarter-inch permanent deflection. It will collapse on you if you add another 50 pounds to that pipe.
Schedule 40 Steel Pipe Chemical Composition
The Schedule 40 pipe’s nominal wall thickness is not the same as the grade. As a result, a pipe schedule’s chemical composition isn’t always uniform.
Schedule 40 pipe, on the other hand, is made of low-carbon steel, often grade A53. The chemical makeup of A53 steel varies based on the type of weld, but type S seamless A53 steel, for example, looks like this.
- Carbon – 0.25% (max)
- Manganese – 0.95% (max)
- Phosphorous – 0.05% (max)
- Sulfur – 0.045% (max)
- Copper – 0.4% (max)
- Nickel – 0.4% (max)
- Chromium – 0.4% (max)
- Molybdenum – 0.15% (max)
- Vanadium – 0.08% (max)
The dimensions, wall thickness, and weight of the Schedule 40 Pipe are listed below.
| Nominal sizes | Outside diameter | Pipe wall thickness | Weight Chart | |||
| inches | OD in inches | OD in mm | inches | mm | lb/ft | kg/m |
| 1/8 | 0.405 | 10.3 | 0.068 | 1.73 | 0.24 | 0.37 |
| 1/4 | 0.540 | 13.7 | 0.088 | 2.24 | 0.42 | 0.84 |
| 1/2 | 0.840 | 21.3 | 0.109 | 2.77 | 0.85 | 1.27 |
| 3/4 | 1.050 | 26.7 | 0.113 | 2.87 | 1.13 | 1.69 |
| 1 | 1.315 | 33.4 | 0.133 | 3.38 | 1.68 | 2.50 |
| 1 1/4 | 1.660 | 42.2 | 0.140 | 3.56 | 2.27 | 3.39 |
| 1 1/2 | 1.900 | 48.3 | 0.145 | 3.68 | 2.72 | 4.05 |
| 2 | 2.375 | 60.3 | 0.154 | 3.91 | 3.65 | 5.44 |
| 2 1/2 | 2.875 | 73.0 | 0.203 | 5.16 | 5.79 | 8.63 |
| 3 | 3.500 | 88.9 | 0.216 | 5.49 | 7.58 | 11.29 |
| 3 1/2 | 4.000 | 101.6 | 0.226 | 5.74 | 9.11 | 13.57 |
| 4 | 4.500 | 114.3 | 0.237 | 6.02 | 10.79 | 16.07 |
| 5 | 5.563 | 141.3 | 0.258 | 6.55 | 14.62 | 21.77 |
| 6 | 6.625 | 168.3 | 0.280 | 7.11 | 18.97 | 28.26 |
| 8 | 8.625 | 219.1 | 0.322 | 8.18 | 28.55 | 42.55 |
| 10 | 10.750 | 273.0 | 0.365 | 9.27 | 40.48 | 60.31 |
| 12 | 12.750 | 323.8 | 0.406 | 10.31 | 53.52 | 79.73 |
| 14 | 14 | 355.6 | 0.375 | 11.13 | 54.57 | 94.55 |
| 16 | 16 | 406.4 | 0.500 | 12.70 | 82.77 | 123.30 |
| 18 | 18 | 457.0 | 0.562 | 14.27 | 104.67 | 155.80 |
| 20 | 20 | 508.0 | 0.594 | 15.09 | 123.11 | 183.42 |
| 24 | 24 | 610.0 | 0.688 | 17.48 | 171.29 | 255.41 |
| 32 | 32 | 813.0 | 0.688 | 17.48 | 230.08 | 342.91 |
A conversion chart below shows the relationship between pipe size, schedules, and wall thicknesses.
| Metric diameter | Inch | Out diameter | Out diameter points to the thickness | ||
| A | B | ASME | STD | SCH40 | SCH80 |
| 8 | 1/4′ | – | – | – | – |
| 10 | 3/8 | – | – | – | – |
| 15 | 1/2″ | 21.3 | 2.77 | 2.77 | 3.73 |
| 20 | 3/4″ | 26.7 | 2.87 | 2.87 | 3.91 |
| 25 | 1″ | 33.4 | 3.38 | 3.38 | 4.55 |
| 32 | 1.1/4″ | 42.2 | 3.56 | 3.56 | 4.85 |
| 40 | 1.1/2″ | 48.3 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 5.08 |
| 50 | 2″ | 60.3 | 3.91 | 3.91 | 5.54 |
| 65 | 2.1/2″ | 73 | 5.16 | 5.16 | 7.01 |
| 80 | 3″ | 88.9 | 5.49 | 5.49 | 7.62 |
| 90 | 3.1/2″ | 101.6 | 5.74 | 5.74 | 8.08 |
| 100 | 4″ | 114.3 | 6.02 | 6.02 | 8.56 |
| 125 | 5″ | 141.3 | 6.55 | 6.55 | 9.53 |
| 150 | 6″ | 168.3 | 7.11 | 7.11 | 10.97 |
| 200 | 8″ | 219.1 | 8.18 | 8.18 | 12.7 |
| 250 | 10″ | 273 | 9.27 | 9.27 | 15.09 |
| 300 | 12″ | 323.8 | 9.53 | 10.31 | 17.48 |
| 350 | 14″ | 355.5 | 9.53 | 11.13 | 19.05 |
| 400 | 16″ | 406.4 | 9.53 | 12.7 | 21.44 |
| 450 | 18″ | 457.2 | 9.53 | 14.27 | 23.83 |
| 500 | 20″ | 508 | 9.53 | 15.09 | 26.19 |
| 550 | 22″ | 558.8 | 9.53 | – | 28.58 |
| 600 | 24″ | 609.6 | 9.53 | 17.48 | 30.96 |
| 650 | 26″ | 660.4 | 9.53 | – | – |
| 700 | 28″ | 711.2 | 9.53 | – | – |
| 750 | 30″ | 762 | 9.53 | – | – |
| 800 | 32″ | 812.8 | 9.53 | 17.48 | – |
| 850 | 34″ | 863.5 | 9.53 | 17.48 | – |
| 900 | 36″ | 914.4 | 9.53 | 19.05 | – |
| 950 | 38″ | 965.2 | 9.53 | – | – |
| 1000 | 40″ | 1016 | 9.53 | – | – |
| 1050 | 42″ | 1066.8 | 9.53 | – | – |
| 1100 | 44″ | 1117.6 | 9.53 | – | – |
| 1150 | 46″ | 1168.4 | 9.53 | – | – |
| 1200 | 48″ | 1219.2 | 9.53 | – | – |
What is the meaning of NPS (Nominal Pipe Size)?
The NPS size refers to a pipe’s the inside diameter (ID), not its exterior diameter (OD). The internal diameter (ID) but not the outside diameter (OD) are affected when the schedule number on a set size is modified (OD). To replace the previously utilised Iron Pipe Sizing, the American Standard Association produced Nominal Pipe Sizing. For high or low-pressure and temperature pipes, this North American standard is employed.
| NPS | OD | SCH | Wall Thickness | ID |
| 1.000” | 1.315” | SCH 40 | 0.133” | 1.049” (approx.) |
| 1.000” | 1.315” | SCH 80 | 0.179” | 0.957” (approx.) |
All pipes are identified by their NPS and Sch numbers. The schedule number is used to estimate the internal diameter.
Pressure Rating for Schedule 40 Carbon Steel Pipe
Steel Piping diameter od chart, wall thickness, and weight per foot are all available for free.
1 in (inch) = 25.4 mm
1 psi (lb/in2) = 6,894.8 Pa (N/m2) = 6.895×10-2 bar
| Maximum Allowable Pressure (psi) (kPa) | ||
| NPS | Outside Diameter (OD) | Schedule |
| (in) | (in)(mm) | 40 |
| 1/4 | 0.5413.7 | 798555057 |
| 3/8 | 0.67517.1 | 660645548 |
| 1/2 | 0.8421.3 | 635843838 |
| 3/4 | 1.0526.7 | 527336357 |
| 1 | 1.31533.4 | 495634172 |
| 1 1/4 | 1.6642.2 | 413328497 |
| 1 1/2 | 1.948.3 | 373925780 |
| 2 | 2.37560.3 | 317721905 |
| 2 1/2 | 2.87573 | 346023857 |
| 3 | 3.588.9 | 302420850 |
| 3 1/2 | 4102 | 276919092 |
| 4 | 4.5114 | 258117796 |
| 5 | 5.563141 | 227315672 |
| 6 | 6.625168 | 207114280 |
| 8 | 8.625219 | 182912611 |
| 10 | 10.75273 | 166411473 |
| 12 | 12.75324 | 156010756 |
| 14 | 14356 | 153310570 |
| 16 | 16406 | 153110556 |
| 18 | 18457 | 153010549 |
| 20 | 20508 | 145510032 |
| 22 | 22559 | |
| 24 | 24610 | 14059687 |
| 30 | 30762 | |
| 32 | 32813 | 10547267 |
| 34 | 34864 | 9926840 |
| 36 | 36914 | 10217040 |
| 42 | 421067 | 8756033 |
Pipe Dimensions and Wall Thickness for Schedule 40
| PipeSizes* | O.D.(in.) | Schedule (40) PipeWall Thickness (in.)** | |
| Sch.40 | |||
| Wall (in) | I.D. (in) | ||
| 1/8″ | 0.41 od | 0.07 in | 0.269 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 0.247 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | |||
| 1/4″ | 0.54 od | 0.090 in | 0.364 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 0.429 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 0.147 lbs/ft | ||
| 3/8″ | 0.675 od | 0.091 in | 0.493 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 0.570 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 0.196 lbs/ft | ||
| 1/2″ | 0.840 od | 0.109 in | 0.622 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 0.850 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 0.294 lbs/ft | ||
| 3/4″ | 1.050 od | 0.113 in | 0.824 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 1.13 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 0.391 | ||
| 1″ | 1.315 od | 0.133 in | 1.049 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 1.68 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 0.581 lbs/ft | ||
| 1-1/4″ | 1.66 od | 0.140 in | 1.380 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 2.27 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 0.785 lbs/ft | ||
| 1-1/2″ | 1.90 od | 0.145 in | 1.610 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 2.72 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 0.939 lbs/ft | ||
| 2″ | 2.375 od | 0.154 in | 2.067 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 3.66 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 1.260 lbs/ft | ||
| 2-1/2″ | 2.875 od | 0.203 in | 2.469 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 5.80 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 2.000 lbs/ft | ||
| 3″ | 3.50 od | 0.216 in | 3.068 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 7.58 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 2.620 lbs/ft | ||
| 3-1/2″ | 4.00 od | 0.226 in | 3.550 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 9.12 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 3.150 lbs/ft | ||
| 4″ | 4.50 od | 0.237 in | 4.026 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 10.80 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 3.730 lbs/ft | ||
| 5″ | 5.563 od | 0.258 in | 5.047 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 14.63 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 5.050 lbs/ft | ||
| 6″ | 6.625 od | 0.280 in | 6.065 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 18.99 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 6.560 lbs/ft | ||
| 8″ | 8.625 od | 0.322 in | 7.981 id |
| Weight(lbs/ft.) | Steel | 28.58 lbs/ft | |
| Stainless | |||
| Aluminum | 9.88 lbs/ft | ||
| *Nominal sizes apply; Pipe Size is a generic Industry Size Standard that is solely used as a guide. ** Each manufacturer’s tolerances may differ slightly. |


SCH 40 Nominal pipe size (NPS)
| NPS | 1/2 | 3/4 | 1 | 1¼ | 1½ | 2 | 2½ | 3 | 3½ | 4 |
| DN | 15 | 20 | 25 | 32 | 40 | 50 | 65 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
Notes:
The corresponding DN = 25 multiplied by the NPS number for NPS 4.
From NPS 12 onwards, the wall thickness between SCH 40 and STD differs, and from NPS 10 onwards, the wall thickness between schedule 80 and XS differs.
In India, you may get 2-inch Schedule 40 galvanized and black steel pipe at a low price.
| INCH | NPS | Schedule 40 ASTM A106/ A53/ API 5L Grade B Seamless Pipe Price |
| MSL | ISMT | JSL | USL | BAO | Lontrin | SMTM | TENARIS | V&M | Wuxi | ||
| 1/2 | 15 | 1,313.53 | 1,316.18 | 1,330.88 | – | 1,029.41 | 1,036.76 | 1,460.59 | 1,396.06 | 1,425.47 | 1,012.06 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 1,112.94 | 1,095.59 | 1,110.29 | – | 954.88 | 963.24 | 1,250.00 | 1,176.47 | 1,205.88 | 938.53 |
| 1 | 25 | 946.88 | 948.53 | 963.24 | – | 881.35 | 889.71 | 1,102.94 | 1,029.41 | 1,058.82 | 875.00 |
| 1.25 | 32 | 911.76 | 904.41 | 919.12 | – | 851.94 | 860.29 | 1,058.82 | 985.29 | 1,014.71 | 845.59 |
| 1.5 | 40 | 818.82 | 821.47 | 816.18 | – | 807.82 | 816.18 | 955.88 | 882.35 | 911.76 | 821.47 |
| 2 | 50 | 799.12 | 786.76 | 821.47 | – | 622.65 | 625.00 | 948.18 | 869.65 | 899.06 | 612.29 |
| 2.5 | 65 | 799.12 | 786.76 | 821.47 | – | 622.65 | 625.00 | 948.18 | 869.65 | 899.06 | 612.29 |
| 3 | 80 | 799.12 | 786.76 | 821.47 | – | 622.65 | 625.00 | 948.18 | 869.65 | 899.06 | 612.29 |
| 3.5 | 90 | 799.12 | 786.76 | 821.47 | – | 622.65 | 625.00 | 948.18 | 869.65 | 899.06 | 612.29 |
| 4 | 100 | 799.12 | 786.76 | 821.47 | 755.29 | 622.65 | 625.00 | 948.18 | 869.65 | 899.06 | 612.29 |
| 5 | 125 | 799.12 | 786.76 | 821.47 | 755.29 | 622.65 | 625.00 | 948.18 | 869.65 | 899.06 | 612.29 |
| 6 | 150 | 799.12 | 786.76 | 821.47 | 755.29 | 622.65 | 625.00 | 948.18 | 869.65 | 899.06 | 612.29 |
| 8 | 200 | 799.12 | 786.76 | 821.47 | 755.29 | 647.06 | 654.41 | 948.18 | 869.65 | 899.06 | 639.71 |
| 10 | 250 | 799.12 | 786.76 | – | 755.29 | 647.06 | 654.41 | 948.18 | 869.65 | 899.06 | 639.71 |
| 12 | 300 | 862.94 | – | – | 755.29 | 647.06 | 654.41 | 1,000.00 | 926.47 | 955.88 | 639.71 |
| 14 | 350 | 862.94 | – | – | 755.29 | 661.76 | 669.12 | 1,000.00 | 926.47 | 955.88 | 654.41 |
| 16 | 400 | 886.35 | – | – | – | 661.76 | 669.12 | 1,029.41 | 955.88 | 985.29 | 654.41 |
| 18 | 450 | 886.35 | – | – | – | 676.47 | 683.82 | 1,029.41 | 955.88 | 985.29 | 669.12 |
| 20 | 500 | 886.35 | – | – | – | 676.47 | 683.82 | 1,029.41 | 955.88 | 985.29 | 669.12 |
| 22 | 550 | – | – | – | – | 705.88 | 713.24 | 1,176.47 | 1,029.41 | 1,132.35 | 698.53 |
| 24 | 600 | – | – | – | – | 705.88 | 713.24 | 1,176.47 | 1,029.41 | 1,132.35 | 698.53 |
Difference Pipe is divided into two schedules: Schedule 40 and Schedule 80.
Pipes in schedules 40 and 80 have a lot in common. They’re so similar that some folks get them mixed up.
The walls of schedule 40 pipe, on the other hand, are thinner than those of schedule 80 pipe. Schedule 80 is often used in commercial applications due to its capacity to resist higher pressures than schedule 40.
How can you tell if a schedule 40 pipe can withstand the pressure?
A mathematical formula can be used to determine if schedule 40 or schedule 80 is better for your project.
(1,000)*(P/S) = SCH
In this equation, P is the pipe’s internal working pressure, and S is the maximum stress that the material can withstand.
If your pipe has an S value of 12,000 and an internal working pressure of 450 psi, for example, your equation is:
37.5 = (1,000) * (450/12,000)
You should be alright with this plan because 37.5 is so close to SCH 40.
Sch 40 Steel Pipe is used in the following industries.
SCH 40 steel pipe is used by many organizations, especially those that need to provide air, gas, or water at high temperatures. The diameter, strength, and reactivity of this scheduled pipe make it a reliable option in construction.
Sch 40 Steel Pipe is used in a variety of applications.
Steel pipes with the schedule 40 designation can be obtained in most hardware stores. This product is popular among DIYers because it may be used in a variety of tasks. Schedule 40 steel tubing is used to make curtain rods, bookcases, coat hooks, floor lights, and magazine racks.
Steel pipe, schedule 40
Of course, scheduled 40 pipes are used by the oil and gas industry to transport high-temperature, high-pressure liquids for commercial and residential constructions.
Steel Pipe Schedule 40 Prices
The cost of the Schedule 40 steel pipe varies significantly based on the length, grade, and volume of the pipe at the time of purchase. If you buy a large number of pipes from a company that specializes in fabrication, like Prashaant Steel & Alloys your costs will be much lower than if you bought the same product from Home Depot.
Read More :
Growing Crude Steel Production in India: According to worldsteel, India’s crude steel production increased by roughly 18% to 118 million tonne (MT) in 2021, while global leader China saw a 3% dip to 1 032.8 MT.


Recent Comments